Synopsis
Nikola Tesla invented alternating current (AC) which allowed no electrical power to be lost when passing through a current.
- Programme: Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
- Episode: The Age of Invention
- Channel: BBC Four
- Broadcast year: 2011
- Physics
Licence: ERA Licence required
UK only
Staff and students of licensed education establishments only
Cannot be adapted
Add Notes
More clips from Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity

2: The Age of Invention | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
2: The Age of Invention | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Jim Al-Khalili shows how harnessing the link between magnetism and electricity transformed the world, allow...

Electricity, Magnetism, Motion | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Electricity, Magnetism, Motion | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Hans Christian Ørsted discovered that an electric current creates a magnetic field.

Electromagnets and telegraphs | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Electromagnets and telegraphs | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Jim Al-Khalili explains how an electromagnet works and how it paved the way for the birth of the tele...
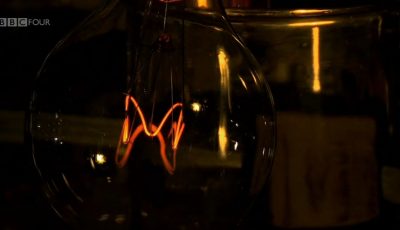
The first light bulbs | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
The first light bulbs | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Jim Al-Khalili explores the history of Thomas Edison's first incandescent light bulb.

2: The Age of Invention | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
2: The Age of Invention | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Jim Al-Khalili shows how harnessing the link between magnetism and electricity transformed the world, allow...

Electricity, Magnetism, Motion | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Electricity, Magnetism, Motion | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Hans Christian Ørsted discovered that an electric current creates a magnetic field.

Electromagnets and telegraphs | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Electromagnets and telegraphs | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Jim Al-Khalili explains how an electromagnet works and how it paved the way for the birth of the tele...
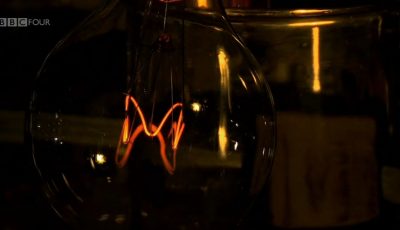
The first light bulbs | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
The first light bulbs | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Jim Al-Khalili explores the history of Thomas Edison's first incandescent light bulb.
More resources about Current, potential difference and resistance

Alternating and direct current | Additional Science 2
Alternating and direct current | Additional Science 2
Spec references J249: P8.2h J250: P6.2g. Alternating and direct current. Description and animation.

Ohm's law | GCSE Bitesize Revision
Ohm's law | GCSE Bitesize Revision
. Ohm's law V = IR with worked example narrated slides.

Positive and negative charges | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Positive and negative charges | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Benjamin Franklin discovered that electricity could be like money in a bank, it could be in credit (p...

Resistance | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Resistance | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Jim Al-Khalili explains how, as we made microchips smaller, the electrical feature of resistance was becoming more probl...

Voltaic Pile | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Voltaic Pile | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Invented by Italian chemist Alessandro Volta in 1799, the voltaic pile was the first electrical battery that could con...

What is electricity | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
What is electricity | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
An electric current is essentially the flow of electrons (which are electrically charged) from one atom to anot...
More from Jim Al-Khalili

2: The Order of the Elements | Chemistry: A Volatile History
2: The Order of the Elements | Chemistry: A Volatile History
Professor Jim Al-Khalili looks at how the early scientists' bid to decode the order of the elements was driven b...

Einstein and the beetle | Gravity and Me: The Force that Shapes our Lives
Einstein and the beetle | Gravity and Me: The Force that Shapes our Lives
Professor Jim Al-Khalili explains Einstein's analogy of gravity that he told his son to explain his...

Prof Jim Al Khalili goes inside Calder Hall for his first look inside the core of a nuclear reactor | Britain's Nuclear Secrets: Inside Sellafield
Prof Jim Al Khalili goes inside Calder Hall for his first look inside the core of a nuclear reactor | Britain's Nuclear Secrets: Inside Sellafield
Nuclear physicist Professo...

Sarah-Jayne Blakemore on teenage brains | The Life Scientific
Sarah-Jayne Blakemore on teenage brains | The Life Scientific
Professor Sarah-Jayne Blakemore talks to Jim Al-Khalili about her research on the developing teenage brain.

Electromagnets and telegraphs | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Electromagnets and telegraphs | Shock and Awe: The Story of Electricity
Jim Al-Khalili explains how an electromagnet works and how it paved the way for the birth of the tele...

Fukushima: Is Nuclear Power Safe? | Horizon
Fukushima: Is Nuclear Power Safe? | Horizon
Six months after the explosions at the Fukushima nuclear plant in Japan, Professor Jim Al-Khalili sets out to discover whether nu...

Al-Khwarizmi's digit and numerical system | Science and Islam
Al-Khwarizmi's digit and numerical system | Science and Islam
Jim Al-Khalili explains how our numerical system spread to Europe through the work of the Arabic mathematician ...

The big bang and the creation of hydrogen and helium | Atom
The big bang and the creation of hydrogen and helium | Atom
George Gamow believed that helium existed in the universe before the sun and the stars were formed.

Electrolysis - Discovery of Potassium | Curriculum Bites
Electrolysis - Discovery of Potassium | Curriculum Bites
Spec references J248: C3.4b J250: C3.4b. Professor Jim Al-Khalili recreates the electrolysis experiment that lead to...
